MS MARCO
MS MARCO Passage Ranking is a large dataset to train models for information retrieval. It consists of about 500k real search queries from Bing search engine with the relevant text passage that answers the query.
This page shows how to train Sparse Encoder models, more precisely a Splade model, on this dataset so that it can be used for searching text passages given queries (key words, phrases or questions).
If you are interested in how to use these models, see Application - Retrieve & Re-Rank.
There are pre-trained models available, which you can directly use without the need of training your own models. For more information, see: Pretrained Models.
This page describes one strategy to train a Splade models on the MS MARCO dataset:
SparseMultipleNegativesRankingLoss
Training code: train_splade_msmarco_mnrl.py
When we use SparseMultipleNegativesRankingLoss, we provide triplets: (query, positive_passage, negative_passage) where positive_passage is the relevant passage to the query and negative_passage is a non-relevant passage to the query. We compute the embeddings for all queries, positive passages, and negative passages in the corpus and then optimize the following objective: The (query, positive_passage) pair must be close in the vector space, while (query, negative_passage) should be distant in vector space.
To further improve the training, we use in-batch negatives:
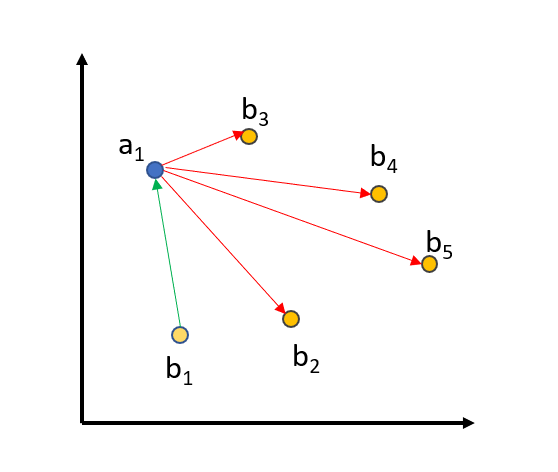
We embed all queries, positive_passages, and negative_passages into the vector space. The matching (query_i, positive_passage_i) should be close, while there should be a large distance between a query and all other (positive/negative) passages from all other triplets in a batch. For a batch size of 64, we compare a query against 64+64=128 passages, from which only one passage should be close and the 127 others should be distant in vector space.
One way to improve training is to choose really good negatives, also know as hard negative: The negative should look really similar to the positive passage, but it should not be relevant to the query.
We find these hard negatives in the following way: We use existing retrieval systems (e.g. lexical search and other bi-encoder retrieval systems), and for each query we find the most relevant passages. We then use a powerful cross-encoder/ms-marco-MiniLM-L6-v2 Cross-Encoder to score the found (query, passage) pairs. We provide scores for 160 million such pairs in our MS MARCO Mined Triplet dataset collection.
For SparseMultipleNegativesRankingLoss, we must ensure that in the triplet (query, positive_passage, negative_passage) that the negative_passage is indeed not relevant for the query. The MS MARCO dataset is sadly highly redundant, and even though that there is on average only one passage marked as relevant for a query, it actually contains many passages that humans would consider as relevant. We must ensure that these passages are not passed as negatives: We do this by ensuring a certain threshold in the CrossEncoder scores between the relevant passages and the mined hard negative. By default, we set a threshold of 3: If the (query, positive_passage) gets a score of 9 from the CrossEncoder, than we will only consider negatives with a score below 6 from the CrossEncoder. This threshold ensures that we actually use negatives in our triplets.
You can find this data by traversing to any of the datasets in the MS MARCO Mined Triplet dataset collection and using the triplet-hard subset. Across all datasets, this refers to 175.7 million triplets. The original data can be found here. For our example we just used the original triplet dataset as it:
from datasets import load_dataset
dataset_size = 100_000 # We only use the first 100k samples for training
print("The dataset has not been fully stored as texts on disk yet. We will do this now.")
corpus = load_dataset("sentence-transformers/msmarco", "corpus", split="train")
corpus = dict(zip(corpus["passage_id"], corpus["passage"]))
queries = load_dataset("sentence-transformers/msmarco", "queries", split="train")
queries = dict(zip(queries["query_id"], queries["query"]))
dataset = load_dataset("sentence-transformers/msmarco", "triplets", split="train")
dataset = dataset.select(range(dataset_size))
def id_to_text_map(batch):
return {
"query": [queries[qid] for qid in batch["query_id"]],
"positive": [corpus[pid] for pid in batch["positive_id"]],
"negative": [corpus[pid] for pid in batch["negative_id"]],
}
dataset = dataset.map(id_to_text_map, batched=True, remove_columns=["query_id", "positive_id", "negative_id"])
dataset = dataset.train_test_split(test_size=10_000)
train_dataset = dataset["train"]
eval_dataset = dataset["test"]