Losses
sentence_transformers.losses defines different loss functions that can be used to fine-tune embedding models on training data. The choice of loss function plays a critical role when fine-tuning the model. It determines how well our embedding model will work for the specific downstream task.
Sadly, there is no “one size fits all” loss function. Which loss function is suitable depends on the available training data and on the target task. Consider checking out the Loss Overview to help narrow down your choice of loss function(s).
BatchAllTripletLoss
- class sentence_transformers.losses.BatchAllTripletLoss(model: ~sentence_transformers.SentenceTransformer.SentenceTransformer, distance_metric=<function BatchHardTripletLossDistanceFunction.eucledian_distance>, margin: float = 5)[source]
BatchAllTripletLoss takes a batch with (sentence, label) pairs and computes the loss for all possible, valid triplets, i.e., anchor and positive must have the same label, anchor and negative a different label. The labels must be integers, with same label indicating sentences from the same class. Your train dataset must contain at least 2 examples per label class.
- Parameters:
model – SentenceTransformer model
distance_metric – Function that returns a distance between two embeddings. The class SiameseDistanceMetric contains pre-defined metrics that can be used.
margin – Negative samples should be at least margin further apart from the anchor than the positive.
References
Source: https://github.com/NegatioN/OnlineMiningTripletLoss/blob/master/online_triplet_loss/losses.py
Paper: In Defense of the Triplet Loss for Person Re-Identification, https://huggingface.co/papers/1703.07737
Blog post: https://omoindrot.github.io/triplet-loss
- Requirements:
Each sentence must be labeled with a class.
Your dataset must contain at least 2 examples per labels class.
- Inputs:
Texts
Labels
single sentences
class
- Recommendations:
Use
BatchSamplers.GROUP_BY_LABEL(docs) to ensure that each batch contains 2+ examples per label class.
- Relations:
BatchHardTripletLossuses only the hardest positive and negative samples, rather than all possible, valid triplets.BatchHardSoftMarginTripletLossuses only the hardest positive and negative samples, rather than all possible, valid triplets. Also, it does not require setting a margin.BatchSemiHardTripletLossuses only semi-hard triplets, valid triplets, rather than all possible, valid triplets.
Example
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, SentenceTransformerTrainer, losses from datasets import Dataset model = SentenceTransformer("microsoft/mpnet-base") # E.g. 0: sports, 1: economy, 2: politics train_dataset = Dataset.from_dict({ "sentence": [ "He played a great game.", "The stock is up 20%", "They won 2-1.", "The last goal was amazing.", "They all voted against the bill.", ], "label": [0, 1, 0, 0, 2], }) loss = losses.BatchAllTripletLoss(model) trainer = SentenceTransformerTrainer( model=model, train_dataset=train_dataset, loss=loss, ) trainer.train()
BatchHardSoftMarginTripletLoss
- class sentence_transformers.losses.BatchHardSoftMarginTripletLoss(model: ~sentence_transformers.SentenceTransformer.SentenceTransformer, distance_metric=<function BatchHardTripletLossDistanceFunction.eucledian_distance>)[source]
BatchHardSoftMarginTripletLoss takes a batch with (sentence, label) pairs and computes the loss for all possible, valid triplets, i.e., anchor and positive must have the same label, anchor and negative a different label. The labels must be integers, with same label indicating sentences from the same class. Your train dataset must contain at least 2 examples per label class. This soft-margin variant does not require setting a margin.
- Parameters:
model – SentenceTransformer model
distance_metric – Function that returns a distance between two embeddings. The class SiameseDistanceMetric contains pre-defined metrics that can be used.
- Definitions:
- Easy triplets:
Triplets which have a loss of 0 because
distance(anchor, positive) + margin < distance(anchor, negative).- Hard triplets:
Triplets where the negative is closer to the anchor than the positive, i.e.,
distance(anchor, negative) < distance(anchor, positive).- Semi-hard triplets:
Triplets where the negative is not closer to the anchor than the positive, but which still have a positive loss, i.e.,
distance(anchor, positive) < distance(anchor, negative) + margin.
References
Source: https://github.com/NegatioN/OnlineMiningTripletLoss/blob/master/online_triplet_loss/losses.py
Paper: In Defense of the Triplet Loss for Person Re-Identification, https://huggingface.co/papers/1703.07737
Blog post: https://omoindrot.github.io/triplet-loss
- Requirements:
Each sentence must be labeled with a class.
Your dataset must contain at least 2 examples per labels class.
Your dataset should contain hard positives and negatives.
- Inputs:
Texts
Labels
single sentences
class
- Recommendations:
Use
BatchSamplers.GROUP_BY_LABEL(docs) to ensure that each batch contains 2+ examples per label class.
- Relations:
BatchHardTripletLossuses a user-specified margin, while this loss does not require setting a margin.
Example
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, SentenceTransformerTrainer, losses from datasets import Dataset model = SentenceTransformer("microsoft/mpnet-base") # E.g. 0: sports, 1: economy, 2: politics train_dataset = Dataset.from_dict({ "sentence": [ "He played a great game.", "The stock is up 20%", "They won 2-1.", "The last goal was amazing.", "They all voted against the bill.", ], "label": [0, 1, 0, 0, 2], }) loss = losses.BatchHardSoftMarginTripletLoss(model) trainer = SentenceTransformerTrainer( model=model, train_dataset=train_dataset, loss=loss, ) trainer.train()
BatchHardTripletLoss
- class sentence_transformers.losses.BatchHardTripletLoss(model: ~sentence_transformers.SentenceTransformer.SentenceTransformer, distance_metric=<function BatchHardTripletLossDistanceFunction.eucledian_distance>, margin: float = 5)[source]
BatchHardTripletLoss takes a batch with (sentence, label) pairs and computes the loss for all possible, valid triplets, i.e., anchor and positive must have the same label, anchor and negative a different label. It then looks for the hardest positive and the hardest negatives. The labels must be integers, with same label indicating sentences from the same class. Your train dataset must contain at least 2 examples per label class.
- Parameters:
model – SentenceTransformer model
distance_metric – Function that returns a distance between two embeddings. The class SiameseDistanceMetric contains pre-defined metrics that can be used
margin – Negative samples should be at least margin further apart from the anchor than the positive.
- Definitions:
- Easy triplets:
Triplets which have a loss of 0 because
distance(anchor, positive) + margin < distance(anchor, negative).- Hard triplets:
Triplets where the negative is closer to the anchor than the positive, i.e.,
distance(anchor, negative) < distance(anchor, positive).- Semi-hard triplets:
Triplets where the negative is not closer to the anchor than the positive, but which still have a positive loss, i.e.,
distance(anchor, positive) < distance(anchor, negative) + margin.
References
Source: https://github.com/NegatioN/OnlineMiningTripletLoss/blob/master/online_triplet_loss/losses.py
Paper: In Defense of the Triplet Loss for Person Re-Identification, https://huggingface.co/papers/1703.07737
Blog post: https://omoindrot.github.io/triplet-loss
- Requirements:
Each sentence must be labeled with a class.
Your dataset must contain at least 2 examples per labels class.
Your dataset should contain hard positives and negatives.
- Inputs:
Texts
Labels
single sentences
class
- Recommendations:
Use
BatchSamplers.GROUP_BY_LABEL(docs) to ensure that each batch contains 2+ examples per label class.
- Relations:
BatchAllTripletLossuses all possible, valid triplets, rather than only the hardest positive and negative samples.BatchSemiHardTripletLossuses only semi-hard triplets, valid triplets, rather than only the hardest positive and negative samples.BatchHardSoftMarginTripletLossdoes not require setting a margin, while this loss does.
Example
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, SentenceTransformerTrainer, losses from datasets import Dataset model = SentenceTransformer("microsoft/mpnet-base") # E.g. 0: sports, 1: economy, 2: politics train_dataset = Dataset.from_dict({ "sentence": [ "He played a great game.", "The stock is up 20%", "They won 2-1.", "The last goal was amazing.", "They all voted against the bill.", ], "label": [0, 1, 0, 0, 2], }) loss = losses.BatchHardTripletLoss(model) trainer = SentenceTransformerTrainer( model=model, train_dataset=train_dataset, loss=loss, ) trainer.train()
BatchSemiHardTripletLoss
- class sentence_transformers.losses.BatchSemiHardTripletLoss(model: ~sentence_transformers.SentenceTransformer.SentenceTransformer, distance_metric=<function BatchHardTripletLossDistanceFunction.eucledian_distance>, margin: float = 5)[source]
BatchSemiHardTripletLoss takes a batch with (label, sentence) pairs and computes the loss for all possible, valid triplets, i.e., anchor and positive must have the same label, anchor and negative a different label. It then looks for the semi hard positives and negatives. The labels must be integers, with same label indicating sentences from the same class. Your train dataset must contain at least 2 examples per label class.
- Parameters:
model – SentenceTransformer model
distance_metric – Function that returns a distance between two embeddings. The class SiameseDistanceMetric contains pre-defined metrics that can be used
margin – Negative samples should be at least margin further apart from the anchor than the positive.
- Definitions:
- Easy triplets:
Triplets which have a loss of 0 because
distance(anchor, positive) + margin < distance(anchor, negative).- Hard triplets:
Triplets where the negative is closer to the anchor than the positive, i.e.,
distance(anchor, negative) < distance(anchor, positive).- Semi-hard triplets:
Triplets where the negative is not closer to the anchor than the positive, but which still have a positive loss, i.e.,
distance(anchor, positive) < distance(anchor, negative) + margin.
References
Source: https://github.com/NegatioN/OnlineMiningTripletLoss/blob/master/online_triplet_loss/losses.py
Paper: In Defense of the Triplet Loss for Person Re-Identification, https://huggingface.co/papers/1703.07737
Blog post: https://omoindrot.github.io/triplet-loss
- Requirements:
Each sentence must be labeled with a class.
Your dataset must contain at least 2 examples per labels class.
Your dataset should contain semi hard positives and negatives.
- Inputs:
Texts
Labels
single sentences
class
- Recommendations:
Use
BatchSamplers.GROUP_BY_LABEL(docs) to ensure that each batch contains 2+ examples per label class.
- Relations:
BatchHardTripletLossuses only the hardest positive and negative samples, rather than only semi hard positive and negatives.BatchAllTripletLossuses all possible, valid triplets, rather than only semi hard positive and negatives.BatchHardSoftMarginTripletLossuses only the hardest positive and negative samples, rather than only semi hard positive and negatives. Also, it does not require setting a margin.
Example
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, SentenceTransformerTrainer, losses from datasets import Dataset model = SentenceTransformer("microsoft/mpnet-base") # E.g. 0: sports, 1: economy, 2: politics train_dataset = Dataset.from_dict({ "sentence": [ "He played a great game.", "The stock is up 20%", "They won 2-1.", "The last goal was amazing.", "They all voted against the bill.", ], "label": [0, 1, 0, 0, 2], }) loss = losses.BatchSemiHardTripletLoss(model) trainer = SentenceTransformerTrainer( model=model, train_dataset=train_dataset, loss=loss, ) trainer.train()
ContrastiveLoss
- class sentence_transformers.losses.ContrastiveLoss(model: ~sentence_transformers.SentenceTransformer.SentenceTransformer, distance_metric=<function SiameseDistanceMetric.<lambda>>, margin: float = 0.5, size_average: bool = True)[source]
Contrastive loss. Expects as input two texts and a label of either 0 or 1. If the label == 1, then the distance between the two embeddings is reduced. If the label == 0, then the distance between the embeddings is increased.
- Parameters:
model – SentenceTransformer model
distance_metric – Function that returns a distance between two embeddings. The class SiameseDistanceMetric contains pre-defined metrices that can be used
margin – Negative samples (label == 0) should have a distance of at least the margin value.
size_average – Average by the size of the mini-batch.
References
Further information: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/4246277_Dimensionality_Reduction_by_Learning_an_Invariant_Mapping
- Requirements:
(anchor, positive/negative) pairs
- Inputs:
Texts
Labels
(anchor, positive/negative) pairs
1 if positive, 0 if negative
- Relations:
OnlineContrastiveLossis similar, but uses hard positive and hard negative pairs. It often yields better results.
Example
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, SentenceTransformerTrainer, losses from datasets import Dataset model = SentenceTransformer("microsoft/mpnet-base") train_dataset = Dataset.from_dict({ "sentence1": ["It's nice weather outside today.", "He drove to work."], "sentence2": ["It's so sunny.", "She walked to the store."], "label": [1, 0], }) loss = losses.ContrastiveLoss(model) trainer = SentenceTransformerTrainer( model=model, train_dataset=train_dataset, loss=loss, ) trainer.train()
OnlineContrastiveLoss
- class sentence_transformers.losses.OnlineContrastiveLoss(model: ~sentence_transformers.SentenceTransformer.SentenceTransformer, distance_metric=<function SiameseDistanceMetric.<lambda>>, margin: float = 0.5)[source]
This Online Contrastive loss is similar to
ConstrativeLoss, but it selects hard positive (positives that are far apart) and hard negative pairs (negatives that are close) and computes the loss only for these pairs. This loss often yields better performances than ContrastiveLoss.- Parameters:
model – SentenceTransformer model
distance_metric – Function that returns a distance between two embeddings. The class SiameseDistanceMetric contains pre-defined metrics that can be used
margin – Negative samples (label == 0) should have a distance of at least the margin value.
References
- Requirements:
(anchor, positive/negative) pairs
Data should include hard positives and hard negatives
- Inputs:
Texts
Labels
(anchor, positive/negative) pairs
1 if positive, 0 if negative
- Relations:
ContrastiveLossis similar, but does not use hard positive and hard negative pairs.OnlineContrastiveLossoften yields better results.
Example
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, SentenceTransformerTrainer, losses from datasets import Dataset model = SentenceTransformer("microsoft/mpnet-base") train_dataset = Dataset.from_dict({ "sentence1": ["It's nice weather outside today.", "He drove to work."], "sentence2": ["It's so sunny.", "She walked to the store."], "label": [1, 0], }) loss = losses.OnlineContrastiveLoss(model) trainer = SentenceTransformerTrainer( model=model, train_dataset=train_dataset, loss=loss, ) trainer.train()
ContrastiveTensionLoss
- class sentence_transformers.losses.ContrastiveTensionLoss(model: SentenceTransformer)[source]
This loss expects only single sentences, without any labels. Positive and negative pairs are automatically created via random sampling, such that a positive pair consists of two identical sentences and a negative pair consists of two different sentences. An independent copy of the encoder model is created, which is used for encoding the first sentence of each pair. The original encoder model encodes the second sentence. The embeddings are compared and scored using the generated labels (1 if positive, 0 if negative) using the binary cross entropy objective.
Note that you must use the ContrastiveTensionDataLoader for this loss. The pos_neg_ratio of the ContrastiveTensionDataLoader can be used to determine the number of negative pairs per positive pair.
Generally,
ContrastiveTensionLossInBatchNegativesis recommended over this loss, as it gives a stronger training signal.- Parameters:
model – SentenceTransformer model
References
Semantic Re-Tuning with Contrastive Tension: https://openreview.net/pdf?id=Ov_sMNau-PF
- Inputs:
Texts
Labels
single sentences
none
- Relations:
ContrastiveTensionLossInBatchNegativesuses in-batch negative sampling, which gives a stronger training signal than this loss.
Example
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, losses from sentence_transformers.losses import ContrastiveTensionDataLoader model = SentenceTransformer('all-MiniLM-L6-v2') train_examples = [ 'This is the 1st sentence', 'This is the 2nd sentence', 'This is the 3rd sentence', 'This is the 4th sentence', 'This is the 5th sentence', 'This is the 6th sentence', 'This is the 7th sentence', 'This is the 8th sentence', 'This is the 9th sentence', 'This is the final sentence', ] train_dataloader = ContrastiveTensionDataLoader(train_examples, batch_size=3, pos_neg_ratio=3) train_loss = losses.ContrastiveTensionLoss(model=model) model.fit( [(train_dataloader, train_loss)], epochs=10, )
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
ContrastiveTensionLossInBatchNegatives
- class sentence_transformers.losses.ContrastiveTensionLossInBatchNegatives(model: ~sentence_transformers.SentenceTransformer.SentenceTransformer, scale: float = 20.0, similarity_fct=<function cos_sim>)[source]
This loss expects only single sentences, without any labels. Positive and negative pairs are automatically created via random sampling, such that a positive pair consists of two identical sentences and a negative pair consists of two different sentences. An independent copy of the encoder model is created, which is used for encoding the first sentence of each pair. The original encoder model encodes the second sentence. Unlike
ContrastiveTensionLoss, this loss uses the batch negative sampling strategy, i.e. the negative pairs are sampled from the batch. Using in-batch negative sampling gives a stronger training signal than the originalContrastiveTensionLoss. The performance usually increases with increasing batch sizes.Note that you should not use the ContrastiveTensionDataLoader for this loss, but just a normal DataLoader with InputExample instances. The two texts of each InputExample instance should be identical.
- Parameters:
model – SentenceTransformer model
scale – Output of similarity function is multiplied by scale value
similarity_fct – similarity function between sentence embeddings. By default, cos_sim. Can also be set to dot product (and then set scale to 1)
References
Semantic Re-Tuning with Contrastive Tension: https://openreview.net/pdf?id=Ov_sMNau-PF
- Relations:
ContrastiveTensionLossdoes not select negative pairs in-batch, resulting in a weaker training signal than this loss.
- Inputs:
Texts
Labels
(anchor, anchor) pairs
none
Example
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, losses from torch.utils.data import DataLoader model = SentenceTransformer('all-MiniLM-L6-v2') train_examples = [ InputExample(texts=['This is a positive pair', 'Where the distance will be minimized'], label=1), InputExample(texts=['This is a negative pair', 'Their distance will be increased'], label=0), ] train_examples = [ InputExample(texts=['This is the 1st sentence', 'This is the 1st sentence']), InputExample(texts=['This is the 2nd sentence', 'This is the 2nd sentence']), InputExample(texts=['This is the 3rd sentence', 'This is the 3rd sentence']), InputExample(texts=['This is the 4th sentence', 'This is the 4th sentence']), InputExample(texts=['This is the 5th sentence', 'This is the 5th sentence']), ] train_dataloader = DataLoader(train_examples, shuffle=True, batch_size=32) train_loss = losses.ContrastiveTensionLossInBatchNegatives(model=model) model.fit( [(train_dataloader, train_loss)], epochs=10, )
CoSENTLoss
- class sentence_transformers.losses.CoSENTLoss(model: ~sentence_transformers.SentenceTransformer.SentenceTransformer, scale: float = 20.0, similarity_fct=<function pairwise_cos_sim>)[source]
This class implements CoSENT (Consistent SENTence embedding) loss. It expects that each of the InputExamples consists of a pair of texts and a float valued label, representing the expected similarity score between the pair.
It computes the following loss function:
loss = logsum(1+exp(s(k,l)-s(i,j))+exp...), where(i,j)and(k,l)are any of the input pairs in the batch such that the expected similarity of(i,j)is greater than(k,l). The summation is over all possible pairs of input pairs in the batch that match this condition.Anecdotal experiments show that this loss function produces a more powerful training signal than
CosineSimilarityLoss, resulting in faster convergence and a final model with superior performance. Consequently, CoSENTLoss may be used as a drop-in replacement forCosineSimilarityLossin any training script.- Parameters:
model – SentenceTransformerModel
similarity_fct – Function to compute the PAIRWISE similarity between embeddings. Default is
util.pairwise_cos_sim.scale – Output of similarity function is multiplied by scale value. Represents the inverse temperature.
References
For further details, see: https://penghao-bdsc.github.io/papers/CoSENT_TASLP2024.pdf
- Requirements:
Sentence pairs with corresponding similarity scores in range of the similarity function. Default is [-1,1].
- Inputs:
Texts
Labels
(sentence_A, sentence_B) pairs
float similarity score
- Relations:
AnglELossis CoSENTLoss withpairwise_angle_simas the metric, rather thanpairwise_cos_sim.CosineSimilarityLossseems to produce a weaker training signal than CoSENTLoss. In our experiments, CoSENTLoss is recommended.
Example
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, SentenceTransformerTrainer, losses from datasets import Dataset model = SentenceTransformer("microsoft/mpnet-base") train_dataset = Dataset.from_dict({ "sentence1": ["It's nice weather outside today.", "He drove to work."], "sentence2": ["It's so sunny.", "She walked to the store."], "score": [1.0, 0.3], }) loss = losses.CoSENTLoss(model) trainer = SentenceTransformerTrainer( model=model, train_dataset=train_dataset, loss=loss, ) trainer.train()
AnglELoss
- class sentence_transformers.losses.AnglELoss(model: SentenceTransformer, scale: float = 20.0)[source]
This class implements AnglE (Angle Optimized) loss. This is a modification of
CoSENTLoss, designed to address the following issue: The cosine function’s gradient approaches 0 as the wave approaches the top or bottom of its form. This can hinder the optimization process, so AnglE proposes to instead optimize the angle difference in complex space in order to mitigate this effect.It expects that each of the InputExamples consists of a pair of texts and a float valued label, representing the expected similarity score between the pair.
It computes the following loss function:
loss = logsum(1+exp(s(i,j)-s(k,l))+exp...), where(i,j)and(k,l)are any of the input pairs in the batch such that the expected similarity of(i,j)is greater than(k,l). The summation is over all possible pairs of input pairs in the batch that match this condition. This is the same as CoSENTLoss, with a different similarity function.- Parameters:
model – SentenceTransformerModel
scale – Output of similarity function is multiplied by scale value. Represents the inverse temperature.
References
For further details, see: https://aclanthology.org/2024.acl-long.101/
- Requirements:
Sentence pairs with corresponding similarity scores in range of the similarity function. Default is [-1,1].
- Inputs:
Texts
Labels
(sentence_A, sentence_B) pairs
float similarity score
- Relations:
CoSENTLossis AnglELoss withpairwise_cos_simas the metric, rather thanpairwise_angle_sim.CosineSimilarityLossseems to produce a weaker training signal thanCoSENTLossorAnglELoss.
Example
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, SentenceTransformerTrainer, losses from datasets import Dataset model = SentenceTransformer("microsoft/mpnet-base") train_dataset = Dataset.from_dict({ "sentence1": ["It's nice weather outside today.", "He drove to work."], "sentence2": ["It's so sunny.", "She walked to the store."], "score": [1.0, 0.3], }) loss = losses.AnglELoss(model) trainer = SentenceTransformerTrainer( model=model, train_dataset=train_dataset, loss=loss, ) trainer.train()
CosineSimilarityLoss
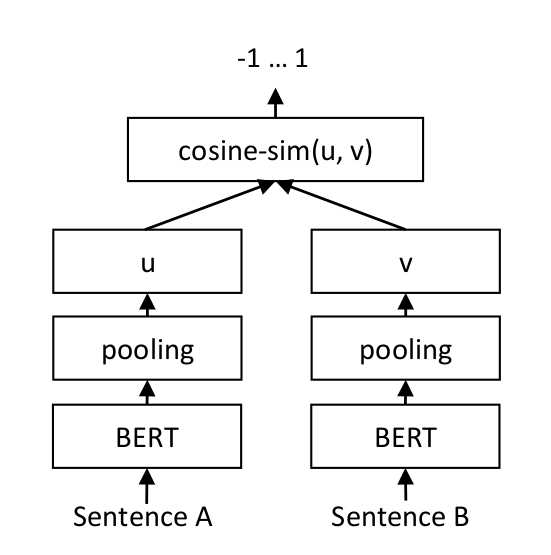
For each sentence pair, we pass sentence A and sentence B through our network which yields the embeddings u und v. The similarity of these embeddings is computed using cosine similarity and the result is compared to the gold similarity score.
This allows our network to be fine-tuned to recognize the similarity of sentences.
- class sentence_transformers.losses.CosineSimilarityLoss(model: SentenceTransformer, loss_fct: Module = MSELoss(), cos_score_transformation: Module = Identity())[source]
CosineSimilarityLoss expects that the InputExamples consists of two texts and a float label. It computes the vectors
u = model(sentence_A)andv = model(sentence_B)and measures the cosine-similarity between the two. By default, it minimizes the following loss:||input_label - cos_score_transformation(cosine_sim(u,v))||_2.- Parameters:
model – SentenceTransformer model
loss_fct – Which pytorch loss function should be used to compare the
cosine_similarity(u, v)with the input_label? By default, MSE is used:||input_label - cosine_sim(u, v)||_2cos_score_transformation – The cos_score_transformation function is applied on top of cosine_similarity. By default, the identify function is used (i.e. no change).
References
- Requirements:
Sentence pairs with corresponding similarity scores in range [0, 1]
- Inputs:
Texts
Labels
(sentence_A, sentence_B) pairs
float similarity score
- Relations:
CoSENTLossseems to produce a stronger training signal than CosineSimilarityLoss. In our experiments, CoSENTLoss is recommended.AnglELossisCoSENTLosswithpairwise_angle_simas the metric, rather thanpairwise_cos_sim. It also produces a stronger training signal than CosineSimilarityLoss.
Example
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, SentenceTransformerTrainer, losses from datasets import Dataset model = SentenceTransformer("microsoft/mpnet-base") train_dataset = Dataset.from_dict({ "sentence1": ["It's nice weather outside today.", "He drove to work."], "sentence2": ["It's so sunny.", "She walked to the store."], "score": [1.0, 0.3], }) loss = losses.CosineSimilarityLoss(model) trainer = SentenceTransformerTrainer( model=model, train_dataset=train_dataset, loss=loss, ) trainer.train()
DenoisingAutoEncoderLoss
- class sentence_transformers.losses.DenoisingAutoEncoderLoss(model: SentenceTransformer, decoder_name_or_path: str | None = None, tie_encoder_decoder: bool = True)[source]
This loss expects as input a pairs of damaged sentences and the corresponding original ones. During training, the decoder reconstructs the original sentences from the encoded sentence embeddings. Here the argument ‘decoder_name_or_path’ indicates the pretrained model (supported by Hugging Face) to be used as the decoder. Since decoding process is included, here the decoder should have a class called XXXLMHead (in the context of Hugging Face’s Transformers). The ‘tie_encoder_decoder’ flag indicates whether to tie the trainable parameters of encoder and decoder, which is shown beneficial to model performance while limiting the amount of required memory. Only when the encoder and decoder are from the same architecture, can the flag ‘tie_encoder_decoder’ work.
The data generation process (i.e. the ‘damaging’ process) has already been implemented in
DenoisingAutoEncoderDataset, allowing you to only provide regular sentences.- Parameters:
model (SentenceTransformer) – The SentenceTransformer model.
decoder_name_or_path (str, optional) – Model name or path for initializing a decoder (compatible with Hugging Face’s Transformers). Defaults to None.
tie_encoder_decoder (bool) – Whether to tie the trainable parameters of encoder and decoder. Defaults to True.
References
- Requirements:
The decoder should have a class called XXXLMHead (in the context of Hugging Face’s Transformers)
Should use a large corpus
- Inputs:
Texts
Labels
(damaged_sentence, original_sentence) pairs
none
sentence fed through
DenoisingAutoEncoderDatasetnone
Example
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, losses from sentence_transformers.datasets import DenoisingAutoEncoderDataset from torch.utils.data import DataLoader model_name = "bert-base-cased" model = SentenceTransformer(model_name) train_sentences = [ "First training sentence", "Second training sentence", "Third training sentence", "Fourth training sentence", ] batch_size = 2 train_dataset = DenoisingAutoEncoderDataset(train_sentences) train_dataloader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, drop_last=True) train_loss = losses.DenoisingAutoEncoderLoss( model, decoder_name_or_path=model_name, tie_encoder_decoder=True ) model.fit( train_objectives=[(train_dataloader, train_loss)], epochs=10, )
GISTEmbedLoss
- class sentence_transformers.losses.GISTEmbedLoss(model: SentenceTransformer, guide: SentenceTransformer, temperature: float = 0.01, margin_strategy: Literal['absolute', 'relative'] = 'absolute', margin: float = 0.0, contrast_anchors: bool = True, contrast_positives: bool = True, gather_across_devices: bool = False)[source]
This loss is used to train a SentenceTransformer model using the GISTEmbed algorithm. It takes a model and a guide model as input, and uses the guide model to guide the in-batch negative sample selection. The cosine similarity is used to compute the loss and the temperature parameter is used to scale the cosine similarities.
You can apply different false-negative filtering strategies to discard hard negatives that are too similar to the positive. Two strategies are supported:
“absolute”: Discards negatives whose similarity score is greater than or equal to
positive_score - margin.“relative”: Discards negatives whose similarity score is greater than or equal to
positive_score * (1 - margin).
- Parameters:
model – SentenceTransformer model based on a transformers model.
guide – SentenceTransformer model to guide the in-batch negative sample selection.
temperature – Temperature parameter to scale the cosine similarities. Inverse of the
scaleparameter inMultipleNegativesRankingLoss.margin_strategy – Strategy used for false negative filtering. One of {“absolute”, “relative”}.
margin – The margin value for filtering negatives. Defaults to 0.0, together with the “absolute” strategy, this only removes negatives that are more similar to the query than the positive is to the query.
contrast_anchors – If True, include anchor-anchor pairs in the loss computation, resulting in the embeddings of the anchors being pushed further apart. Defaults to True, following the original GISTEmbed paper.
contrast_positives – If True, include positive-positive pairs in the loss computation, resulting in the embeddings of the positives being pushed further apart. Defaults to True, following the original GISTEmbed paper, but setting to False may yield better results in some retrieval tasks.
gather_across_devices – If True, gather the embeddings across all devices before computing the loss. Recommended when training on multiple GPUs, as it allows for larger batch sizes, but it may slow down training due to communication overhead, and can potentially lead to out-of-memory errors.
References
For further details, see: https://huggingface.co/papers/2402.16829
- Requirements:
(anchor, positive, negative) triplets
(anchor, positive) pairs
- Inputs:
Texts
Labels
(anchor, positive, negative) triplets
none
(anchor, positive) pairs
none
- Recommendations:
Use
BatchSamplers.NO_DUPLICATES(docs) to ensure that no in-batch negatives are duplicates of the anchor or positive samples.
- Relations:
MultipleNegativesRankingLossis similar to this loss, but it does not use a guide model to guide the in-batch negative sample selection. GISTEmbedLoss yields a stronger training signal at the cost of some training overhead.
Example
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, SentenceTransformerTrainer, losses from datasets import Dataset model = SentenceTransformer("microsoft/mpnet-base") guide = SentenceTransformer("all-MiniLM-L6-v2") train_dataset = Dataset.from_dict({ "anchor": ["It's nice weather outside today.", "He drove to work."], "positive": ["It's so sunny.", "He took the car to the office."], }) loss = losses.GISTEmbedLoss(model, guide) trainer = SentenceTransformerTrainer( model=model, train_dataset=train_dataset, loss=loss, ) trainer.train()
CachedGISTEmbedLoss
- class sentence_transformers.losses.CachedGISTEmbedLoss(model: SentenceTransformer, guide: SentenceTransformer, temperature: float = 0.01, mini_batch_size: int = 32, show_progress_bar: bool = False, margin_strategy: Literal['absolute', 'relative'] = 'absolute', margin: float = 0.0, contrast_anchors: bool = True, contrast_positives: bool = True, gather_across_devices: bool = False)[source]
This loss is a combination of
GISTEmbedLossandCachedMultipleNegativesRankingLoss. Typically,MultipleNegativesRankingLossrequires a larger batch size for better performance.GISTEmbedLossyields stronger training signals thanMultipleNegativesRankingLossdue to the use of a guide model for in-batch negative sample selection. Meanwhile,CachedMultipleNegativesRankingLossallows for scaling of the batch size by dividing the computation into two stages of embedding and loss calculation, which both can be scaled by mini-batches (https://huggingface.co/papers/2101.06983).By combining the guided selection from
GISTEmbedLossand Gradient Cache fromCachedMultipleNegativesRankingLoss, it is possible to reduce memory usage while maintaining performance levels comparable to those ofGISTEmbedLoss.You can apply different false-negative filtering strategies to discard hard negatives that are too similar to the positive. Two strategies are supported:
“absolute”: Discards negatives whose similarity score is greater than or equal to
positive_score - margin.“relative”: Discards negatives whose similarity score is greater than or equal to
positive_score * (1 - margin).
- Parameters:
model – SentenceTransformer model
guide – SentenceTransformer model to guide the in-batch negative sample selection.
temperature – Temperature parameter to scale the cosine similarities.
mini_batch_size – Mini-batch size for the forward pass, this denotes how much memory is actually used during training and evaluation. The larger the mini-batch size, the more memory efficient the training is, but the slower the training will be. It’s recommended to set it as high as your GPU memory allows. The default value is 32.
show_progress_bar – If True, a progress bar for the mini-batches is shown during training. The default is False.
margin_strategy – Strategy used for false negative filtering. One of {“absolute”, “relative”}.
margin – The margin value for filtering negatives. Defaults to 0.0, together with the “absolute” strategy, this only removes negatives that are more similar to the query than the positive is to the query.
contrast_anchors – If True, include anchor-anchor pairs in the loss computation, resulting in the embeddings of the anchors being pushed further apart. Defaults to True, following the original GISTEmbed paper.
contrast_positives – If True, include positive-positive pairs in the loss computation, resulting in the embeddings of the positives being pushed further apart. Defaults to True, following the original GISTEmbed paper, but setting to False may yield better results in some retrieval tasks.
gather_across_devices – If True, gather the embeddings across all devices before computing the loss. Recommended when training on multiple GPUs, as it allows for larger batch sizes, but it may slow down training due to communication overhead, and can potentially lead to out-of-memory errors.
References
Efficient Natural Language Response Suggestion for Smart Reply, Section 4.4: https://huggingface.co/papers/1705.00652
Scaling Deep Contrastive Learning Batch Size under Memory Limited Setup: https://huggingface.co/papers/2101.06983
GISTEmbed: Guided In-sample Selection of Training Negatives for Text Embedding Fine-tuning https://huggingface.co/papers/2402.16829
- Requirements:
(anchor, positive) pairs or (anchor, positive, negative pairs)
Should be used with large batch sizes for superior performance, but has slower training time than
MultipleNegativesRankingLoss
- Inputs:
Texts
Labels
(anchor, positive) pairs
none
(anchor, positive, negative) triplets
none
(anchor, positive, negative_1, …, negative_n)
none
- Recommendations:
Use
BatchSamplers.NO_DUPLICATES(docs) to ensure that no in-batch negatives are duplicates of the anchor or positive samples.
- Relations:
Equivalent to
GISTEmbedLoss, but with caching that allows for much higher batch sizes
Example
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, SentenceTransformerTrainer, losses from datasets import Dataset model = SentenceTransformer("microsoft/mpnet-base") guide = SentenceTransformer("all-MiniLM-L6-v2") train_dataset = Dataset.from_dict({ "anchor": ["It's nice weather outside today.", "He drove to work."], "positive": ["It's so sunny.", "He took the car to the office."], }) loss = losses.CachedGISTEmbedLoss( model, guide, mini_batch_size=64, margin_strategy="absolute", # or "relative" (e.g., margin=0.05 for max. 95% of positive similarity) margin=0.1 ) trainer = SentenceTransformerTrainer( model=model, train_dataset=train_dataset, loss=loss, ) trainer.train()
MSELoss
- class sentence_transformers.losses.MSELoss(model: SentenceTransformer)[source]
Computes the MSE loss between the computed sentence embedding and a target sentence embedding. This loss is used when extending sentence embeddings to new languages as described in our publication Making Monolingual Sentence Embeddings Multilingual using Knowledge Distillation.
For an example, see the distillation documentation on extending language models to new languages.
- Parameters:
model – SentenceTransformerModel
References
Making Monolingual Sentence Embeddings Multilingual using Knowledge Distillation: https://huggingface.co/papers/2004.09813
- Requirements:
Usually uses a finetuned teacher M in a knowledge distillation setup
- Inputs:
Texts
Labels
sentence
model sentence embeddings
sentence_1, sentence_2, …, sentence_N
model sentence embeddings
- Relations:
MarginMSELossis equivalent to this loss, but with a margin through a negative pair.
Example
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, SentenceTransformerTrainer, losses from datasets import Dataset student_model = SentenceTransformer("microsoft/mpnet-base") teacher_model = SentenceTransformer("all-mpnet-base-v2") train_dataset = Dataset.from_dict({ "english": ["The first sentence", "The second sentence", "The third sentence", "The fourth sentence"], "french": ["La première phrase", "La deuxième phrase", "La troisième phrase", "La quatrième phrase"], }) def compute_labels(batch): return { "label": teacher_model.encode(batch["english"]) } train_dataset = train_dataset.map(compute_labels, batched=True) loss = losses.MSELoss(student_model) trainer = SentenceTransformerTrainer( model=student_model, train_dataset=train_dataset, loss=loss, ) trainer.train()
MarginMSELoss
- class sentence_transformers.losses.MarginMSELoss(model: ~sentence_transformers.SentenceTransformer.SentenceTransformer, similarity_fct=<function pairwise_dot_score>)[source]
Compute the MSE loss between the
|sim(Query, Pos) - sim(Query, Neg)|and|gold_sim(Query, Pos) - gold_sim(Query, Neg)|. By default, sim() is the dot-product. The gold_sim is often the similarity score from a teacher model.In contrast to
MultipleNegativesRankingLoss, the two passages do not have to be strictly positive and negative, both can be relevant or not relevant for a given query. This can be an advantage of MarginMSELoss over MultipleNegativesRankingLoss, but note that the MarginMSELoss is much slower to train. With MultipleNegativesRankingLoss, with a batch size of 64, we compare one query against 128 passages. With MarginMSELoss, we compare a query only against two passages. It’s also possible to use multiple negatives with MarginMSELoss, but the training would be even slower to train.- Parameters:
model – SentenceTransformerModel
similarity_fct – Which similarity function to use.
References
For more details, please refer to https://huggingface.co/papers/2010.02666.
- Requirements:
(query, passage_one, passage_two) triplets or (query, positive, negative_1, …, negative_n)
Usually used with a finetuned teacher M in a knowledge distillation setup
- Inputs:
Texts
Labels
(query, passage_one, passage_two) triplets
M(query, passage_one) - M(query, passage_two)
(query, passage_one, passage_two) triplets
[M(query, passage_one), M(query, passage_two)]
(query, positive, negative_1, …, negative_n)
[M(query, positive) - M(query, negative_i) for i in 1..n]
(query, positive, negative_1, …, negative_n)
[M(query, positive), M(query, negative_1), …, M(query, negative_n)]
- Relations:
MSELossis similar to this loss, but without a margin through the negative pair.
Example
With gold labels, e.g. if you have hard scores for sentences. Imagine you want a model to embed sentences with similar “quality” close to each other. If the “text1” has quality 5 out of 5, “text2” has quality 1 out of 5, and “text3” has quality 3 out of 5, then the similarity of a pair can be defined as the difference of the quality scores. So, the similarity between “text1” and “text2” is 4, and the similarity between “text1” and “text3” is 2. If we use this as our “Teacher Model”, the label becomes similraity(“text1”, “text2”) - similarity(“text1”, “text3”) = 4 - 2 = 2.
Positive values denote that the first passage is more similar to the query than the second passage, while negative values denote the opposite.
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, SentenceTransformerTrainer, losses from datasets import Dataset model = SentenceTransformer("microsoft/mpnet-base") train_dataset = Dataset.from_dict({ "text1": ["It's nice weather outside today.", "He drove to work."], "text2": ["It's so sunny.", "He took the car to work."], "text3": ["It's very sunny.", "She walked to the store."], "label": [0.1, 0.8], }) loss = losses.MarginMSELoss(model) trainer = SentenceTransformerTrainer( model=model, train_dataset=train_dataset, loss=loss, ) trainer.train()
We can also use a teacher model to compute the similarity scores. In this case, we can use the teacher model to compute the similarity scores and use them as the silver labels. This is often used in knowledge distillation.
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, SentenceTransformerTrainer, losses from datasets import Dataset student_model = SentenceTransformer("microsoft/mpnet-base") teacher_model = SentenceTransformer("all-mpnet-base-v2") train_dataset = Dataset.from_dict({ "query": ["It's nice weather outside today.", "He drove to work."], "passage1": ["It's so sunny.", "He took the car to work."], "passage2": ["It's very sunny.", "She walked to the store."], }) def compute_labels(batch): emb_queries = teacher_model.encode(batch["query"]) emb_passages1 = teacher_model.encode(batch["passage1"]) emb_passages2 = teacher_model.encode(batch["passage2"]) return { "label": teacher_model.similarity_pairwise(emb_queries, emb_passages1) - teacher_model.similarity_pairwise(emb_queries, emb_passages2) } train_dataset = train_dataset.map(compute_labels, batched=True) loss = losses.MarginMSELoss(student_model) trainer = SentenceTransformerTrainer( model=student_model, train_dataset=train_dataset, loss=loss, ) trainer.train()
We can also use multiple negatives during the knowledge distillation.
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, SentenceTransformerTrainer, losses from datasets import Dataset import torch student_model = SentenceTransformer("microsoft/mpnet-base") teacher_model = SentenceTransformer("all-mpnet-base-v2") train_dataset = Dataset.from_dict( { "query": ["It's nice weather outside today.", "He drove to work."], "passage1": ["It's so sunny.", "He took the car to work."], "passage2": ["It's very cold.", "She walked to the store."], "passage3": ["Its rainy", "She took the bus"], } ) def compute_labels(batch): emb_queries = teacher_model.encode(batch["query"]) emb_passages1 = teacher_model.encode(batch["passage1"]) emb_passages2 = teacher_model.encode(batch["passage2"]) emb_passages3 = teacher_model.encode(batch["passage3"]) return { "label": torch.stack( [ teacher_model.similarity_pairwise(emb_queries, emb_passages1) - teacher_model.similarity_pairwise(emb_queries, emb_passages2), teacher_model.similarity_pairwise(emb_queries, emb_passages1) - teacher_model.similarity_pairwise(emb_queries, emb_passages3), ], dim=1, ) } train_dataset = train_dataset.map(compute_labels, batched=True) loss = losses.MarginMSELoss(student_model) trainer = SentenceTransformerTrainer(model=student_model, train_dataset=train_dataset, loss=loss) trainer.train()
MatryoshkaLoss
- class sentence_transformers.losses.MatryoshkaLoss(model: SentenceTransformer, loss: Module, matryoshka_dims: Sequence[int], matryoshka_weights: Sequence[float] | Sequence[int] | None = None, n_dims_per_step: int = -1)[source]
The MatryoshkaLoss can be seen as a loss modifier that allows you to use other loss functions at various different embedding dimensions. This is useful for when you want to train a model where users have the option to lower the embedding dimension to improve their embedding comparison speed and costs.
This loss is also compatible with the Cached… losses, which are in-batch negative losses that allow for higher batch sizes. The higher batch sizes allow for more negatives, and often result in a stronger model.
- Parameters:
model – SentenceTransformer model
loss – The loss function to be used, e.g.
MultipleNegativesRankingLoss,CoSENTLoss, etc.matryoshka_dims – A list of embedding dimensions to be used for the loss function, e.g. [768, 512, 256, 128, 64].
matryoshka_weights – A list of weights to be used for the loss function, e.g. [1, 1, 1, 1, 1]. If None, then the weights will be set to 1 for all dimensions.
n_dims_per_step – The number of dimensions to use per step. If -1, then all dimensions are used. If > 0, then a random sample of n_dims_per_step dimensions are used per step. The default value is -1.
References
The concept was introduced in this paper: https://huggingface.co/papers/2205.13147
- Inputs:
Texts
Labels
any
any
- Relations:
Matryoshka2dLossuses this loss in combination withAdaptiveLayerLosswhich allows forlayer reduction for faster inference.
Example
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, SentenceTransformerTrainer, losses from datasets import Dataset model = SentenceTransformer("microsoft/mpnet-base") train_dataset = Dataset.from_dict({ "anchor": ["It's nice weather outside today.", "He drove to work."], "positive": ["It's so sunny.", "He took the car to the office."], }) loss = losses.MultipleNegativesRankingLoss(model) loss = losses.MatryoshkaLoss(model, loss, [768, 512, 256, 128, 64]) trainer = SentenceTransformerTrainer( model=model, train_dataset=train_dataset, loss=loss, ) trainer.train()
Matryoshka2dLoss
- class sentence_transformers.losses.Matryoshka2dLoss(model: SentenceTransformer, loss: Module, matryoshka_dims: list[int], matryoshka_weights: list[float | int] | None = None, n_layers_per_step: int = 1, n_dims_per_step: int = 1, last_layer_weight: float = 1.0, prior_layers_weight: float = 1.0, kl_div_weight: float = 1.0, kl_temperature: float = 0.3)[source]
The Matryoshka2dLoss can be seen as a loss modifier that combines the
AdaptiveLayerLossand theMatryoshkaLoss. This allows you to train an embedding model that 1) allows users to specify the number of model layers to use, and 2) allows users to specify the output dimensions to use.The former is useful for when you want users to have the option to lower the number of layers used to improve their inference speed and memory usage, and the latter is useful for when you want users to have the option to lower the output dimensions to improve the efficiency of their downstream tasks (e.g. retrieval) or to lower their storage costs.
Note, this uses n_layers_per_step=1 and n_dims_per_step=1 as default, following the original 2DMSE implementation.
- Parameters:
model – SentenceTransformer model
loss – The loss function to be used, e.g.
MultipleNegativesRankingLoss,CoSENTLoss, etc.matryoshka_dims – A list of embedding dimensions to be used for the loss function, e.g. [768, 512, 256, 128, 64].
matryoshka_weights – A list of weights to be used for the loss function, e.g. [1, 1, 1, 1, 1]. If None, then the weights will be set to 1 for all dimensions.
n_layers_per_step – The number of layers to use per step. If -1, then all layers are used. If > 0, then a random sample of n_layers_per_step layers are used per step. The 2DMSE paper uses n_layers_per_step=1. The default value is -1.
n_dims_per_step – The number of dimensions to use per step. If -1, then all dimensions are used. If > 0, then a random sample of n_dims_per_step dimensions are used per step. The default value is -1.
last_layer_weight – The weight to use for the loss of the final layer. Increase this to focus more on the performance when using all layers. The default value is 1.0.
prior_layers_weight – The weight to use for the loss of the prior layers. Increase this to focus more on the performance when using fewer layers. The default value is 1.0.
kl_div_weight – The weight to use for the KL-divergence loss that is used to make the prior layers match that of the last layer. Increase this to focus more on the performance when using fewer layers. The default value is 1.0.
kl_temperature – The temperature to use for the KL-divergence loss. If 0, then the KL-divergence loss is not used. The default value is 1.0.
References
See the 2D Matryoshka Sentence Embeddings (2DMSE) paper: https://huggingface.co/papers/2402.14776
- Requirements:
The base loss cannot be
CachedMultipleNegativesRankingLoss,CachedMultipleNegativesSymmetricRankingLoss, orCachedGISTEmbedLoss.
- Inputs:
Texts
Labels
any
any
- Relations:
MatryoshkaLossis used in this loss, and it is responsible for the dimensionality reduction.AdaptiveLayerLossis used in this loss, and it is responsible for the layer reduction.
Example
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, SentenceTransformerTrainer, losses from datasets import Dataset model = SentenceTransformer("microsoft/mpnet-base") train_dataset = Dataset.from_dict({ "anchor": ["It's nice weather outside today.", "He drove to work."], "positive": ["It's so sunny.", "He took the car to the office."], }) loss = losses.MultipleNegativesRankingLoss(model) loss = losses.Matryoshka2dLoss(model, loss, [768, 512, 256, 128, 64]) trainer = SentenceTransformerTrainer( model=model, train_dataset=train_dataset, loss=loss, ) trainer.train()
AdaptiveLayerLoss
- class sentence_transformers.losses.AdaptiveLayerLoss(model: SentenceTransformer, loss: nn.Module, n_layers_per_step: int = 1, last_layer_weight: float = 1.0, prior_layers_weight: float = 1.0, kl_div_weight: float = 1.0, kl_temperature: float = 0.3)[source]
The AdaptiveLayerLoss can be seen as a loss modifier that allows you to use other loss functions at non-final layers of the Sentence Transformer model. This is useful for when you want to train a model where users have the option to lower the number of layers used to improve their inference speed and memory usage.
- Parameters:
model – SentenceTransformer model
loss – The loss function to be used, e.g.
MultipleNegativesRankingLoss,CoSENTLoss, etc.n_layers_per_step – The number of layers to use per step. If -1, then all layers are used. If > 0, then a random sample of n_layers_per_step layers are used per step, separate from the final layer, which is always used. The 2DMSE paper uses n_layers_per_step=1. The default value is 1.
last_layer_weight – The weight to use for the loss of the final layer. Increase this to focus more on the performance when using all layers. The default value is 1.0.
prior_layers_weight – The weight to use for the loss of the prior layers. Increase this to focus more on the performance when using fewer layers. The default value is 1.0.
kl_div_weight – The weight to use for the KL-divergence loss that is used to make the prior layers match that of the last layer. Increase this to focus more on the performance when using fewer layers. The default value is 1.0.
kl_temperature – The temperature to use for the KL-divergence loss. If 0, then the KL-divergence loss is not used. The default value is 1.0.
References
The concept was inspired by the 2DMSE paper: https://huggingface.co/papers/2402.14776
- Requirements:
The base loss cannot be
CachedMultipleNegativesRankingLoss,CachedMultipleNegativesSymmetricRankingLoss, orCachedGISTEmbedLoss.
- Inputs:
Texts
Labels
any
any
- Relations:
Matryoshka2dLossuses this loss in combination withMatryoshkaLosswhich allows foroutput dimensionality reduction for faster downstream tasks (e.g. retrieval).
Example
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, SentenceTransformerTrainer, losses from datasets import Dataset model = SentenceTransformer("microsoft/mpnet-base") train_dataset = Dataset.from_dict({ "anchor": ["It's nice weather outside today.", "He drove to work."], "positive": ["It's so sunny.", "He took the car to the office."], }) loss = losses.MultipleNegativesRankingLoss(model=model) loss = losses.AdaptiveLayerLoss(model, loss) trainer = SentenceTransformerTrainer( model=model, train_dataset=train_dataset, loss=loss, ) trainer.train()
MegaBatchMarginLoss
- class sentence_transformers.losses.MegaBatchMarginLoss(model: SentenceTransformer, positive_margin: float = 0.8, negative_margin: float = 0.3, use_mini_batched_version: bool = True, mini_batch_size: int = 50)[source]
Given a large batch (like 500 or more examples) of (anchor_i, positive_i) pairs, find for each pair in the batch the hardest negative, i.e. find j != i such that cos_sim(anchor_i, positive_j) is maximal. Then create from this a triplet (anchor_i, positive_i, positive_j) where positive_j serves as the negative for this triplet.
Then train as with the triplet loss.
- Parameters:
model – SentenceTransformerModel
positive_margin – Positive margin, cos(anchor, positive) should be > positive_margin
negative_margin – Negative margin, cos(anchor, negative) should be < negative_margin
use_mini_batched_version – As large batch sizes require a lot of memory, we can use a mini-batched version. We break down the large batch into smaller batches with fewer examples.
mini_batch_size – Size for the mini-batches. Should be a divisor for the batch size in your data loader.
References
This loss function was inspired by the ParaNMT paper: https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/P18-1042/
- Requirements:
(anchor, positive) pairs
Large batches (500 or more examples)
- Inputs:
Texts
Labels
(anchor, positive) pairs
none
- Recommendations:
Use
BatchSamplers.NO_DUPLICATES(docs) to ensure that no in-batch negatives are duplicates of the anchor or positive samples.
Example
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, SentenceTransformerTrainingArguments, SentenceTransformerTrainer, losses from datasets import Dataset train_batch_size = 250 train_mini_batch_size = 32 model = SentenceTransformer('all-MiniLM-L6-v2') train_dataset = Dataset.from_dict({ "anchor": [f"This is sentence number {i}" for i in range(500)], "positive": [f"This is sentence number {i}" for i in range(1, 501)], }) loss = losses.MegaBatchMarginLoss(model=model, mini_batch_size=train_mini_batch_size) args = SentenceTransformerTrainingArguments( output_dir="output", per_device_train_batch_size=train_batch_size, ) trainer = SentenceTransformerTrainer( model=model, args=args, train_dataset=train_dataset, loss=loss, ) trainer.train()
MultipleNegativesRankingLoss
MultipleNegativesRankingLoss is a great loss function if you only have positive pairs, for example, only pairs of similar texts like pairs of paraphrases, pairs of duplicate questions, pairs of (query, response), or pairs of (source_language, target_language).
- class sentence_transformers.losses.MultipleNegativesRankingLoss(model: ~sentence_transformers.SentenceTransformer.SentenceTransformer, scale: float = 20.0, similarity_fct=<function cos_sim>, gather_across_devices: bool = False)[source]
Given a list of (anchor, positive) pairs or (anchor, positive, negative) triplets, this loss optimizes the following:
Given an anchor (e.g. a question), assign the highest similarity to the corresponding positive (i.e. answer) out of every single positive and negative (e.g. all answers) in the batch.
If you provide the optional negatives, they will all be used as extra options from which the model must pick the correct positive. Within reason, the harder this “picking” is, the stronger the model will become. Because of this, a higher batch size results in more in-batch negatives, which then increases performance (to a point).
This loss function works great to train embeddings for retrieval setups where you have positive pairs (e.g. (query, answer)) as it will sample in each batch
n-1negative docs randomly.This loss is also known as InfoNCE loss, SimCSE loss, Cross-Entropy Loss with in-batch negatives, or simply in-batch negatives loss.
- Parameters:
model – SentenceTransformer model
scale – Output of similarity function is multiplied by scale value. In some literature, the scaling parameter is referred to as temperature, which is the inverse of the scale. In short: scale = 1 / temperature, so scale=20.0 is equivalent to temperature=0.05.
similarity_fct – similarity function between sentence embeddings. By default, cos_sim. Can also be set to dot product (and then set scale to 1)
gather_across_devices – If True, gather the embeddings across all devices before computing the loss. Recommended when training on multiple GPUs, as it allows for larger batch sizes, but it may slow down training due to communication overhead, and can potentially lead to out-of-memory errors.
References
Efficient Natural Language Response Suggestion for Smart Reply, Section 4.4: https://huggingface.co/papers/1705.00652
- Requirements:
(anchor, positive) pairs or (anchor, positive, negative) triplets
- Inputs:
Texts
Labels
(anchor, positive) pairs
none
(anchor, positive, negative) triplets
none
(anchor, positive, negative_1, …, negative_n)
none
- Recommendations:
Use
BatchSamplers.NO_DUPLICATES(docs) to ensure that no in-batch negatives are duplicates of the anchor or positive samples.
- Relations:
CachedMultipleNegativesRankingLossis equivalent to this loss, but it uses caching that allows for much higher batch sizes (and thus better performance) without extra memory usage. However, it is slightly slower.MultipleNegativesSymmetricRankingLossis equivalent to this loss, but with an additional loss term.GISTEmbedLossis equivalent to this loss, but uses a guide model to guide the in-batch negative sample selection. GISTEmbedLoss yields a stronger training signal at the cost of some training overhead.
Example
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, SentenceTransformerTrainer, losses from datasets import Dataset model = SentenceTransformer("microsoft/mpnet-base") train_dataset = Dataset.from_dict({ "anchor": ["It's nice weather outside today.", "He drove to work."], "positive": ["It's so sunny.", "He took the car to the office."], }) loss = losses.MultipleNegativesRankingLoss(model) trainer = SentenceTransformerTrainer( model=model, train_dataset=train_dataset, loss=loss, ) trainer.train()
CachedMultipleNegativesRankingLoss
- class sentence_transformers.losses.CachedMultipleNegativesRankingLoss(model: SentenceTransformer, scale: float = 20.0, similarity_fct: callable[[Tensor, Tensor], Tensor] = <function cos_sim>, mini_batch_size: int = 32, gather_across_devices: bool = False, show_progress_bar: bool = False)[source]
Boosted version of MultipleNegativesRankingLoss (https://huggingface.co/papers/1705.00652) by GradCache (https://huggingface.co/papers/2101.06983).
Constrastive learning (here our MNRL loss) with in-batch negatives is usually hard to work with large batch sizes due to (GPU) memory limitation. Even with batch-scaling methods like gradient-scaling, it cannot work either. This is because the in-batch negatives make the data points within the same batch non-independent and thus the batch cannot be broke down into mini-batches. GradCache is a smart way to solve this problem. It achieves the goal by dividing the computation into two stages of embedding and loss calculation, which both can be scaled by mini-batches. As a result, memory of constant size (e.g. that works with batch size = 32) can now process much larger batches (e.g. 65536).
In detail:
It first does a quick embedding step without gradients/computation graphs to get all the embeddings;
Calculate the loss, backward up to the embeddings and cache the gradients wrt. to the embeddings;
A 2nd embedding step with gradients/computation graphs and connect the cached gradients into the backward chain.
Notes: All steps are done with mini-batches. In the original implementation of GradCache, (2) is not done in mini-batches and requires a lot memory when the batch size is large. One drawback is about the speed. Gradient caching will sacrifice around 20% computation time according to the paper.
- Parameters:
model – SentenceTransformer model
scale – Output of similarity function is multiplied by scale value. In some literature, the scaling parameter is referred to as temperature, which is the inverse of the scale. In short: scale = 1 / temperature, so scale=20.0 is equivalent to temperature=0.05.
similarity_fct – similarity function between sentence embeddings. By default, cos_sim. Can also be set to dot product (and then set scale to 1)
mini_batch_size – Mini-batch size for the forward pass, this denotes how much memory is actually used during training and evaluation. The larger the mini-batch size, the more memory efficient the training is, but the slower the training will be. It’s recommended to set it as high as your GPU memory allows. The default value is 32.
gather_across_devices – If True, gather the embeddings across all devices before computing the loss. Recommended when training on multiple GPUs, as it allows for larger batch sizes, but it may slow down training due to communication overhead, and can potentially lead to out-of-memory errors.
show_progress_bar – If True, a progress bar for the mini-batches is shown during training. The default is False.
References
Efficient Natural Language Response Suggestion for Smart Reply, Section 4.4: https://huggingface.co/papers/1705.00652
Scaling Deep Contrastive Learning Batch Size under Memory Limited Setup: https://huggingface.co/papers/2101.06983
- Requirements:
(anchor, positive) pairs or (anchor, positive, negative pairs)
Should be used with large per_device_train_batch_size and low mini_batch_size for superior performance, but slower training time than
MultipleNegativesRankingLoss.
- Inputs:
Texts
Labels
(anchor, positive) pairs
none
(anchor, positive, negative) triplets
none
(anchor, positive, negative_1, …, negative_n)
none
- Recommendations:
Use
BatchSamplers.NO_DUPLICATES(docs) to ensure that no in-batch negatives are duplicates of the anchor or positive samples.
- Relations:
Equivalent to
MultipleNegativesRankingLoss, but with caching that allows for much higher batch sizes (and thus better performance) without extra memory usage. This loss also trains roughly 2x to 2.4x slower thanMultipleNegativesRankingLoss.
Example
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, SentenceTransformerTrainer, losses from datasets import Dataset model = SentenceTransformer("microsoft/mpnet-base") train_dataset = Dataset.from_dict({ "anchor": ["It's nice weather outside today.", "He drove to work."], "positive": ["It's so sunny.", "He took the car to the office."], }) loss = losses.CachedMultipleNegativesRankingLoss(model, mini_batch_size=64) trainer = SentenceTransformerTrainer( model=model, train_dataset=train_dataset, loss=loss, ) trainer.train()
MultipleNegativesSymmetricRankingLoss
- class sentence_transformers.losses.MultipleNegativesSymmetricRankingLoss(model: ~sentence_transformers.SentenceTransformer.SentenceTransformer, scale: float = 20.0, similarity_fct=<function cos_sim>, gather_across_devices: bool = False)[source]
Given a list of (anchor, positive) pairs, this loss sums the following two losses:
Forward loss: Given an anchor, find the sample with the highest similarity out of all positives in the batch. This is equivalent to
MultipleNegativesRankingLoss.Backward loss: Given a positive, find the sample with the highest similarity out of all anchors in the batch.
For example with question-answer pairs,
MultipleNegativesRankingLossjust computes the loss to find the answer given a question, butMultipleNegativesSymmetricRankingLossadditionally computes the loss to find the question given an answer.Note: If you pass triplets, the negative entry will be ignored. A anchor is just searched for the positive.
- Parameters:
model – SentenceTransformer model
scale – Output of similarity function is multiplied by scale value. In some literature, the scaling parameter is referred to as temperature, which is the inverse of the scale. In short: scale = 1 / temperature, so scale=20.0 is equivalent to temperature=0.05.
similarity_fct – similarity function between sentence embeddings. By default, cos_sim. Can also be set to dot product (and then set scale to 1)
gather_across_devices – If True, gather the embeddings across all devices before computing the loss. Recommended when training on multiple GPUs, as it allows for larger batch sizes, but it may slow down training due to communication overhead, and can potentially lead to out-of-memory errors.
- Requirements:
(anchor, positive) pairs
- Inputs:
Texts
Labels
(anchor, positive) pairs
none
- Recommendations:
Use
BatchSamplers.NO_DUPLICATES(docs) to ensure that no in-batch negatives are duplicates of the anchor or positive samples.
- Relations:
Like
MultipleNegativesRankingLoss, but with an additional loss term.CachedMultipleNegativesSymmetricRankingLossis equivalent to this loss, but it uses caching that allows for much higher batch sizes (and thus better performance) without extra memory usage. However, it is slightly slower.
Example
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, SentenceTransformerTrainer, losses from datasets import Dataset model = SentenceTransformer("microsoft/mpnet-base") train_dataset = Dataset.from_dict({ "anchor": ["It's nice weather outside today.", "He drove to work."], "positive": ["It's so sunny.", "He took the car to the office."], }) loss = losses.MultipleNegativesSymmetricRankingLoss(model) trainer = SentenceTransformerTrainer( model=model, train_dataset=train_dataset, loss=loss, ) trainer.train()
CachedMultipleNegativesSymmetricRankingLoss
- class sentence_transformers.losses.CachedMultipleNegativesSymmetricRankingLoss(model: SentenceTransformer, scale: float = 20.0, similarity_fct: callable[[Tensor, Tensor], Tensor] = <function cos_sim>, mini_batch_size: int = 32, gather_across_devices: bool = False, show_progress_bar: bool = False)[source]
Boosted version of
MultipleNegativesSymmetricRankingLoss(MNSRL) by GradCache (https://huggingface.co/papers/2101.06983).Given a list of (anchor, positive) pairs, MNSRL sums the following two losses:
Forward loss: Given an anchor, find the sample with the highest similarity out of all positives in the batch.
Backward loss: Given a positive, find the sample with the highest similarity out of all anchors in the batch.
For example with question-answer pairs, the forward loss finds the answer for a given question and the backward loss finds the question for a given answer. This loss is common in symmetric tasks, such as semantic textual similarity.
The caching modification allows for large batch sizes (which give a better training signal) with constant memory usage, allowing you to reach optimal training signal with regular hardware.
Note: If you pass triplets, the negative entry will be ignored. An anchor is just searched for the positive.
- Parameters:
model – SentenceTransformer model
scale – Output of similarity function is multiplied by scale value. In some literature, the scaling parameter is referred to as temperature, which is the inverse of the scale. In short: scale = 1 / temperature, so scale=20.0 is equivalent to temperature=0.05.
similarity_fct – similarity function between sentence embeddings. By default, cos_sim. Can also be set to dot product (and then set scale to 1)
mini_batch_size – Mini-batch size for the forward pass, this denotes how much memory is actually used during training and evaluation. The larger the mini-batch size, the more memory efficient the training is, but the slower the training will be. It’s recommended to set it as high as your GPU memory allows. The default value is 32.
gather_across_devices – If True, gather the embeddings across all devices before computing the loss. Recommended when training on multiple GPUs, as it allows for larger batch sizes, but it may slow down training due to communication overhead, and can potentially lead to out-of-memory errors.
show_progress_bar – If True, a progress bar for the mini-batches is shown during training. The default is False.
- Requirements:
(anchor, positive) pairs
Should be used with large batch sizes for superior performance, but has slower training time than non-cached versions
- Inputs:
Texts
Labels
(anchor, positive) pairs
none
- Recommendations:
Use
BatchSamplers.NO_DUPLICATES(docs) to ensure that no in-batch negatives are duplicates of the anchor or positive samples.
- Relations:
Like
MultipleNegativesRankingLoss, but with an additional symmetric loss term and caching mechanism.Inspired by
CachedMultipleNegativesRankingLoss, adapted for symmetric loss calculation.
Example
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, SentenceTransformerTrainer, losses from datasets import Dataset model = SentenceTransformer("microsoft/mpnet-base") train_dataset = Dataset.from_dict({ "anchor": ["It's nice weather outside today.", "He drove to work."], "positive": ["It's so sunny.", "He took the car to the office."], }) loss = losses.CachedMultipleNegativesSymmetricRankingLoss(model, mini_batch_size=32) trainer = SentenceTransformerTrainer( model=model, train_dataset=train_dataset, loss=loss, ) trainer.train()
References
Efficient Natural Language Response Suggestion for Smart Reply, Section 4.4: https://huggingface.co/papers/1705.00652
Scaling Deep Contrastive Learning Batch Size under Memory Limited Setup: https://huggingface.co/papers/2101.06983
SoftmaxLoss
- class sentence_transformers.losses.SoftmaxLoss(model: SentenceTransformer, sentence_embedding_dimension: int, num_labels: int, concatenation_sent_rep: bool = True, concatenation_sent_difference: bool = True, concatenation_sent_multiplication: bool = False, loss_fct: Callable = CrossEntropyLoss())[source]
This loss was used in our SBERT publication (https://huggingface.co/papers/1908.10084) to train the SentenceTransformer model on NLI data. It adds a softmax classifier on top of the output of two transformer networks.
MultipleNegativesRankingLossis an alternative loss function that often yields better results, as per https://huggingface.co/papers/2004.09813.- Parameters:
model (SentenceTransformer) – The SentenceTransformer model.
sentence_embedding_dimension (int) – The dimension of the sentence embeddings.
num_labels (int) – The number of different labels.
concatenation_sent_rep (bool) – Whether to concatenate vectors u,v for the softmax classifier. Defaults to True.
concatenation_sent_difference (bool) – Whether to add abs(u-v) for the softmax classifier. Defaults to True.
concatenation_sent_multiplication (bool) – Whether to add u*v for the softmax classifier. Defaults to False.
loss_fct (Callable) – Custom pytorch loss function. If not set, uses nn.CrossEntropyLoss(). Defaults to nn.CrossEntropyLoss().
References
Sentence-BERT: Sentence Embeddings using Siamese BERT-Networks: https://huggingface.co/papers/1908.10084
- Requirements:
sentence pairs with a class label
- Inputs:
Texts
Labels
(sentence_A, sentence_B) pairs
class
Example
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, SentenceTransformerTrainer, losses from datasets import Dataset model = SentenceTransformer("microsoft/mpnet-base") train_dataset = Dataset.from_dict({ "sentence1": [ "A person on a horse jumps over a broken down airplane.", "A person on a horse jumps over a broken down airplane.", "A person on a horse jumps over a broken down airplane.", "Children smiling and waving at camera", ], "sentence2": [ "A person is training his horse for a competition.", "A person is at a diner, ordering an omelette.", "A person is outdoors, on a horse.", "There are children present.", ], "label": [1, 2, 0, 0], }) loss = losses.SoftmaxLoss(model, model.get_sentence_embedding_dimension(), num_labels=3) trainer = SentenceTransformerTrainer( model=model, train_dataset=train_dataset, loss=loss, ) trainer.train()
TripletLoss
- class sentence_transformers.losses.TripletLoss(model: ~sentence_transformers.SentenceTransformer.SentenceTransformer, distance_metric=<function TripletDistanceMetric.<lambda>>, triplet_margin: float = 5)[source]
This class implements triplet loss. Given a triplet of (anchor, positive, negative), the loss minimizes the distance between anchor and positive while it maximizes the distance between anchor and negative. It compute the following loss function:
loss = max(||anchor - positive|| - ||anchor - negative|| + margin, 0).Margin is an important hyperparameter and needs to be tuned respectively.
- Parameters:
model – SentenceTransformerModel
distance_metric – Function to compute distance between two embeddings. The class TripletDistanceMetric contains common distance metrices that can be used.
triplet_margin – The negative should be at least this much further away from the anchor than the positive.
References
For further details, see: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triplet_loss
- Requirements:
(anchor, positive, negative) triplets
- Inputs:
Texts
Labels
(anchor, positive, negative) triplets
none
Example
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, SentenceTransformerTrainer, losses from datasets import Dataset model = SentenceTransformer("microsoft/mpnet-base") train_dataset = Dataset.from_dict({ "anchor": ["It's nice weather outside today.", "He drove to work."], "positive": ["It's so sunny.", "He took the car to the office."], "negative": ["It's quite rainy, sadly.", "She walked to the store."], }) loss = losses.TripletLoss(model=model) trainer = SentenceTransformerTrainer( model=model, train_dataset=train_dataset, loss=loss, ) trainer.train()
DistillKLDivLoss
- class sentence_transformers.losses.DistillKLDivLoss(model: ~sentence_transformers.SentenceTransformer.SentenceTransformer, similarity_fct=<function pairwise_dot_score>, temperature: float = 1.0)[source]
Compute the KL divergence loss between probability distributions derived from student and teacher models’ similarity scores. By default, similarity is calculated using the dot-product. This loss is designed for knowledge distillation where a smaller student model learns from a more powerful teacher model.
The loss computes softmax probabilities from the teacher similarity scores and log-softmax probabilities from the student model, then calculates the KL divergence between these distributions.
- Parameters:
model – SentenceTransformer model (student model)
similarity_fct – Which similarity function to use for the student model
temperature – Temperature parameter to soften probability distributions (higher temperature = softer distributions) A temperature of 1.0 does not scale the scores. Note: in the v5.0.1 release, the default temperature was changed from 2.0 to 1.0.
References
For more details, please refer to https://huggingface.co/papers/2010.11386
- Requirements:
(query, positive, negative_1, …, negative_n) examples
Labels containing teacher model’s scores between query-positive and query-negative pairs
- Inputs:
Texts
Labels
(query, positive, negative)
[Teacher(query, positive), Teacher(query, negative)]
(query, positive, negative_1, …, negative_n)
[Teacher(query, positive), Teacher(query, negative_i)…]
- Relations:
Similar to
MarginMSELossbut uses KL divergence instead of MSEMore suited for distillation tasks where preserving ranking is important
Example
Using a teacher model to compute similarity scores for distillation:
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, SentenceTransformerTrainer, losses from datasets import Dataset import torch student_model = SentenceTransformer("microsoft/mpnet-base") teacher_model = SentenceTransformer("all-mpnet-base-v2") train_dataset = Dataset.from_dict({ "query": ["It's nice weather outside today.", "He drove to work."], "positive": ["It's so sunny.", "He took the car to work."], "negative": ["It's very cold.", "She walked to the store."], }) def compute_labels(batch): emb_queries = teacher_model.encode(batch["query"]) emb_positives = teacher_model.encode(batch["positive"]) emb_negatives = teacher_model.encode(batch["negative"]) pos_scores = teacher_model.similarity_pairwise(emb_queries, emb_positives) neg_scores = teacher_model.similarity_pairwise(emb_queries, emb_negatives) # Stack the scores for positive and negative pairs return { "label": torch.stack([pos_scores, neg_scores], dim=1) } train_dataset = train_dataset.map(compute_labels, batched=True) loss = losses.DistillKLDivLoss(student_model) trainer = SentenceTransformerTrainer(model=student_model, train_dataset=train_dataset, loss=loss) trainer.train()
With multiple negatives:
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, SentenceTransformerTrainer, losses from datasets import Dataset import torch student_model = SentenceTransformer("microsoft/mpnet-base") teacher_model = SentenceTransformer("all-mpnet-base-v2") train_dataset = Dataset.from_dict( { "query": ["It's nice weather outside today.", "He drove to work."], "positive": ["It's so sunny.", "He took the car to work."], "negative1": ["It's very cold.", "She walked to the store."], "negative2": ["Its rainy", "She took the bus"], } ) def compute_labels(batch): emb_queries = teacher_model.encode(batch["query"]) emb_positives = teacher_model.encode(batch["positive"]) emb_negatives1 = teacher_model.encode(batch["negative1"]) emb_negatives2 = teacher_model.encode(batch["negative2"]) pos_scores = teacher_model.similarity_pairwise(emb_queries, emb_positives) neg_scores1 = teacher_model.similarity_pairwise(emb_queries, emb_negatives1) neg_scores2 = teacher_model.similarity_pairwise(emb_queries, emb_negatives2) # Stack the scores for positive and multiple negative pairs return { "label": torch.stack([pos_scores, neg_scores1, neg_scores2], dim=1) } train_dataset = train_dataset.map(compute_labels, batched=True) loss = losses.DistillKLDivLoss(student_model) trainer = SentenceTransformerTrainer(model=student_model, train_dataset=train_dataset, loss=loss) trainer.train()