Retrieve & Re-Rank
In Semantic Search we have shown how to use SentenceTransformer to compute embeddings for queries, sentences, and paragraphs and how to use this for semantic search. For complex search tasks, for example question answering retrieval, the search can significantly be improved by using Retrieve & Re-Rank.
Retrieve & Re-Rank Pipeline
The following pipeline for Information Retrieval / Question Answering Retrieval works very well. All components are provided and explained in this article:
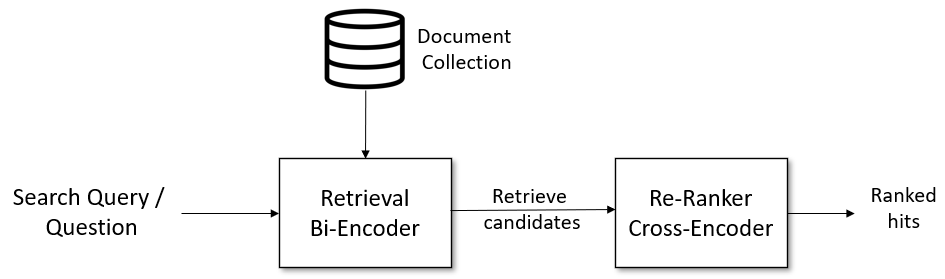
Given a search query, we first use a retrieval system that retrieves a large list of e.g. 100 possible hits which are potentially relevant for the query. For the retrieval, we can use either lexical search, e.g. with a vector engine like Elasticsearch, or we can use dense retrieval with a SentenceTransformer (a.k.a. bi-encoder). However, the retrieval system might retrieve documents that are not that relevant for the search query. Hence, in a second stage, we use a re-ranker based on a CrossEncoder that scores the relevancy of all candidates for the given search query. The output will be a ranked list of hits we can present to the user.
Retrieval: Bi-Encoder
For the retrieval of the candidate set, we can either use lexical search (e.g. Elasticsearch), or we can use a bi-encoder which is implemented in Sentence Transformers.
Lexical search looks for literal matches of the query words in your document collection. It will not recognize synonyms, acronyms or spelling variations. In contrast, semantic search (or dense retrieval) encodes the search query into vector space and retrieves the document embeddings that are close in vector space.
Semantic search overcomes the shortcomings of lexical search and can recognize synonym and acronyms. Have a look at the semantic search article for different options to implement semantic search.
Re-Ranker: Cross-Encoder
The retriever has to be efficient for large document collections with millions of entries. However, it might return irrelevant candidates. A re-ranker based on a Cross-Encoder can substantially improve the final results for the user. The query and a possible document is passed simultaneously to transformer network, which then outputs a single score between 0 and 1 indicating how relevant the document is for the given query.
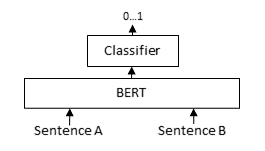
The advantage of Cross-Encoders is the higher performance, as they perform attention across the query and the document. Scoring thousands or millions of (query, document)-pairs would be rather slow. Hence, we use the retriever to create a set of e.g. 100 possible candidates which are then re-ranked by the Cross-Encoder.
Example Scripts
retrieve_rerank_simple_wikipedia.ipynb [ Colab Version ]: This script uses the smaller Simple English Wikipedia as document collection to provide answers to user questions / search queries. First, we split all Wikipedia articles into paragraphs and encode them with a bi-encoder. If a new query / question is entered, it is encoded by the same bi-encoder and the paragraphs with the highest cosine-similarity are retrieved (see semantic search). Next, the retrieved candidates are scored by a Cross-Encoder re-ranker and the 5 passages with the highest score from the Cross-Encoder are presented to the user.
in_document_search_crossencoder.py: If you only have a small set of paragraphs, we don’t do the retrieval stage. This is for example the case if you want to perform search within a single document. In this example, we take the Wikipedia article about Europe and split it into paragraphs. Then, the search query / question and all paragraphs are scored using the Cross-Encoder re-ranker. The most relevant passages for the query are returned.
Pre-trained Bi-Encoders (Retrieval)
The bi-encoder produces embeddings independently for your paragraphs and for your search queries. You can use it like this:
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer
model = SentenceTransformer("multi-qa-mpnet-base-dot-v1")
docs = [
"My first paragraph. That contains information",
"Python is a programming language.",
]
document_embeddings = model.encode(docs)
query = "What is Python?"
query_embedding = model.encode(query)
For more details how to compare the embeddings, see semantic search.
We provide pre-trained models based on:
MS MARCO: 500k real user queries from Bing search engine. See MS MARCO models
Pre-trained Cross-Encoders (Re-Ranker)
For pre-trained Cross Encoder models, see: MS MARCO Cross-Encoders